
SaaS Due Diligence Services: Specialized Team for Software Companies
05/24/2022
How to Structure an Earn Out When Buying an Online Business
07/14/2022Private SaaS firms are usually valued on either revenue multiple, a seller discretionary earnings multiple (or SDE), or for more mature SaaS businesses, EBITDA multiples.
More often that not, SaaS business valuation will incorporate all of these different elements based on a set of factors that a SaaS investor or buyer deems important. The hottest public SaaS companies may sometimes trade at over 20 times revenue but they’re the exception, not the rule.
Most private businesses on a revenue based valuation will likely fall within a 2x to 8x ARR range, the higher end of that range already being a great achievement for the founder of any software companies.
Private SaaS companies are most often valued on revenue (ARR) multiples and Seller Discretionary Earnings (SDE)
As for any M&A transaction or investment, doing proper due diligence and conducting a financial due diligence on the target business is a requirement that no serious investment professional would ever overlook.
To do that you can either rely on your experience buying businesses, learn how to do financial due diligence, or hire professional financial due diligence experts that will deliver a clear and exhaustive report on the financial situation of the business
However software businesses and subscription-based business models have a lot of specific metrics and points of attention to pay particular attention to.
At HoriZen Transaction Services we’ve been reviewing and analyzing SaaS companies, SaaS operation metrics and SaaS financials on a daily basis for years.
Here are the main drivers of value to analyze as part of your due diligence which are directly correlated to the SaaS revenue multiples and investor will be willing to pay.
1 – Lead Generation and Customer Acquisition Channels: How Many Leads Does The Business Attract?

The capacity for a SaaS startup or a bootstrapped SaaS business to attract traffic and leads into has a significant impact on the revenue multiples investors are willing to pay.
Even if the business is not mature in terms of monetization strategy, a SaaS investor or strategic buyer may have a way to benefit from the company’s existing traffic.
For instance, if the demographics of the website visitors perfectly fit the buyer personae of a strategic buyer, the buyer may see extra value in the deal by benefiting from a reduction of their customer acquisition cost post-deal.
What acquisition channels are used, how much is invested in each of these, understanding how dependent these acquisition channels are on third party algorithms (e.g. google ranking algorithm or Facebook ads algorithm) and how scalable they are should be questions you should ask as part of your digital marketing due diligence process.
For enterprise customers, generally the sales process requires sales people to be involved, contrarily to SaaS sales models targeting smaller businesses and who have a no or low-touch sales process where all interactions with a prospective and new customers happen automatically, and monthly recurring revenue or annual recurring revenue are automatically charged to the user credit card.
For enterprise software business, the capacity of the sales team to have a strong lead generation from outreach can also be assessed.
2 – Conversion Rate: How Effective Is The Company At Converting Leads To Use Their SaaS Platform?

The value of a SaaS business is also dependent on the capacity of the team to turn traffic and leads into paid customers.
There are several SaaS operation metrics that you can track and look at to assess the efficiency of the sales and marketing tactics of the target company.
You can start by looking at the sales funnel and break down the conversion rate at each step of the process.
From 100 leads, how many sign up for a free trial? Out of the free trial, how many sign-up for a paid subscription? And how many on paid subscription subsequently decide to upgrade?
To assess the quality of the product and how well it reached market fit, you can also analyze the utilization rate of the product. How many times or hours per week do paid customers use the product?
You can also use this opportunity to better understand what features customers use the most. This information would not necessarily impact business valuation, however it is useful to know to correctly assess market substitutes and to efficiently manage the business post-acquisition.
3 – Monetization: How Is The SaaS business Model Generating Revenue From Customers?
Since median Saas valuation multiple is directly correlated to revenue growth rate, the capacity of a SaaS business to properly monetize their users and optimize the cash generation per user is a key element to take into account to choose what revenue multiple to use.
SaaS companies can generate high cash flow thanks to a limited fixed cost base and generally high gross profit margins. However having a lot of traffic and a lot of users do not necessarily translate into significant revenue if the business and pricing model is not on point.
If this is the case with the target company you’re reviewing, where for instance they use a freemium model but only a very small portion of free users convert into paid user, it may either be an indication that the conversion can be optimized through better pricing management or free vs. paid feature management, or it can be an indication that the market is not really ready to pay for the product.
In any case, even if it represents an opportunity if you are better experienced in these matters than the seller, having a low conversion rate from free to paid will likely impact the revenue multiples that an investor would be ready to pay
4 – Churn and Retention: How Well Does The SaaS Business Retain Customers?
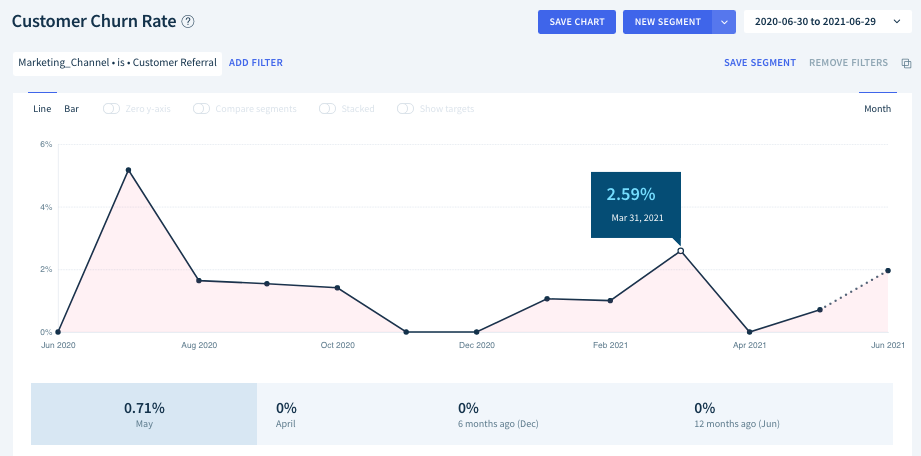
One of the valuation factor that may impact Saas valuation the most is the level of churn. The whole value and attractiveness of most SaaS businesses relie on the recurring revenue that the business generate, which in turn directly impact Saas valuations and revenue multiples.
However if the churn of a subscription business is too high, it becomes harder to consider the nature of revenue as recurring. Let’s put it that way, if most customers churn after 3 months, how is it really different from a 3-month one-off service provider?
A high churn generally means a low Lifetime Customer Value (or LCV), and most of the profitability of a SaaS company relies on its capacity to generate a high lifetime value / CAC.
There are different ways to calculate churn and different platforms out there like Profitwell or ChartMogul that automatically calculate churn, reactivation, upsell and so on, but you do need to understand their lifetime value and churn calculation methodology to drive the right conclusions.
Overall, what we recommend is to look at churn on a cohort basis. This will allow you to spot any recent change in new customer behavior that may have an impact on revenue multiples.
5 – Profitability and Quality of Earnings: How Profitable is the SaaS Business Model?
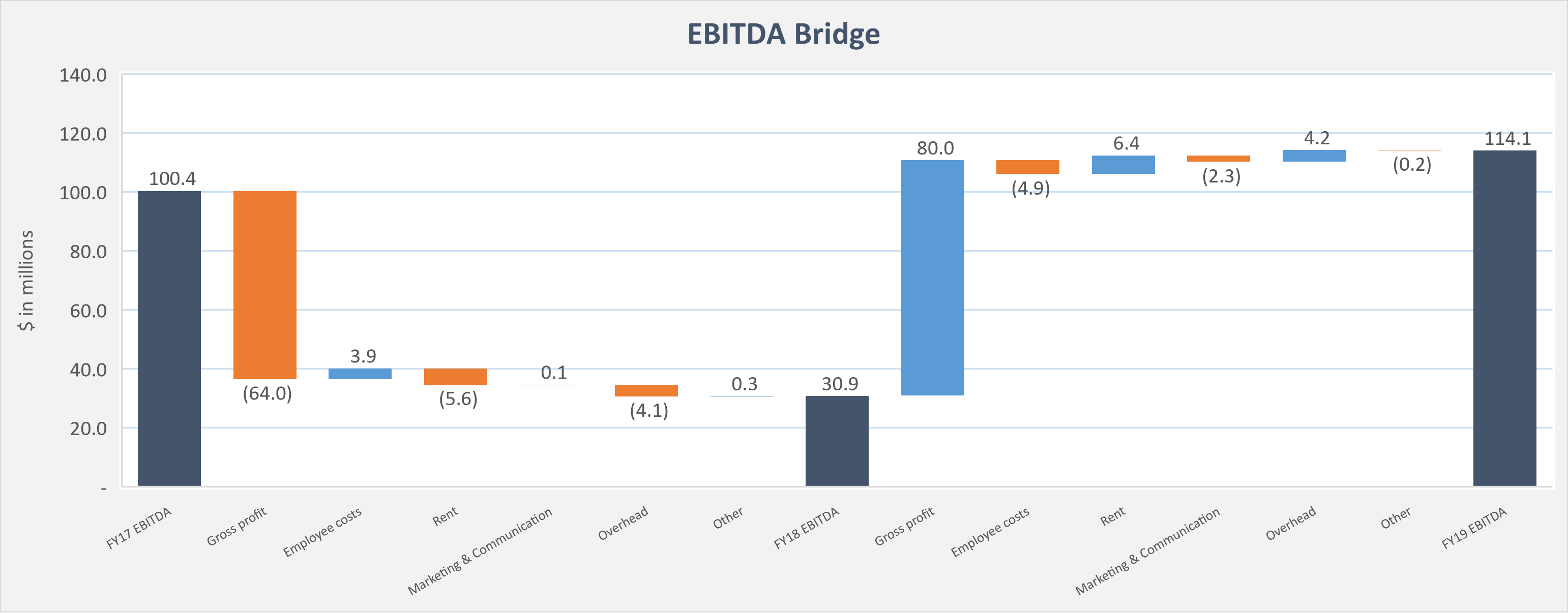
Some well known public Saas companies have remained unprofitable years after their IPO and still trade at high. However, the purpose of every company is to reach the point where they will turn a profit on an annual basis.
A lot of private investors outside the Venture Capitalism world will not invest into a SaaS business if it is not already profitable. And the revenue multiple and EBITDA multiple that they will agree to pay will depends on the level of profitability of the company.
However it is important to keep in mind that as a general rule, the faster a company grows, the harder it is to turn a huge profit in parallel.
Indeed, in a very schematic way, SaaS owners will spend cash on acquiring customers, be it through hiring new sales rep or through increase digital marketing spend.
If the company has a decent retention rate, these newly acquired customers will generate revenue over several years.
From a P&L perspective, that means that an online subscription or software business when it grows fast has to incur all the acquisition costs upfront while the revenue will be recognized over several years.
That also means that if a SaaS company stops spending in digital marketing and just carry on with their existing customer base, they will turn a huge profit, but should see a growth deceleration.
Every business also experience spends that are not core to the business (e.g leasing of the owner’s brand new sports car showing up in the books) or not recurring in nature (e.g. a once in a lifetime fire destroyed 1/10 of the inventory, or the team’s week away in Ibiza to celebrate the 10th anniversary of the business).
It is very important for a buyer or an investor to spot, flag and understand these items. The analysis that consists in listing all the relevant point an suggest adjustments is called a Quality of Earnings (QofE) analysis and this is often the core piece of a financial due diligence report.
The quality of earnings, showing a normalized, adjusted Ebitda, and sometimes a proforma Ebitda or even a stand-alone Ebitda, directly impact the SaaS valuation and what revenue multiple an investor or strategic buyer is willing to pay to acquire the target SaaS business.
If you’re interested in the subject, you can refer to Pierre-Alexandre Heurtebize’s article on Quality of Earnings which has been published on the TechCrunch website. It will also help you better understand how we work at HoriZen Transaction Services when we perform a due diligence and review financials of a SaaS company.
6 – Revenue Concentration Risk: How Diversified is the Recurring Revenue of the SaaS Business?
Revenue concentration is an important red flag to be wary of. And not only for the reasons you believe. Revenue concentration reflects a situation in which one or a handful of customers represent a significant share of the total revenue generated by the target SaaS business
The most common understanding of the risk associated with revenue concentration is the danger of losing one of these customers post-deal and end up with an ARR a fourth lower than when you bought the business. The less common understanding of revenue concentration is the impact it has on the churn rate of a SaaS company.
As a quick example, let’s assume a company doing $1M in MRR, $500k of which are made from two large customers.
If the company claims a 1% monthly gross churn rate, which is a decent gross churn rate in the world of SaaS, we can assume that in absolute value churned customers represent on average $10k each month. (10k/1M = 1%).
But if we treat the two big customers separately as they likely have a specific relationship with the target and a special treatment, then monthly churn rate actually represents $10k / $500k = 2%. And a 2% monthly gross churn, twice as much as the 1% initially presented, makes the business significantly less attractive.
7 – Cash Flow Generation: How Well is the Business Converting Revenue Into Cash Flow?
For both private Saas companies and public Saas companies, the end goal of a business is ultimately to generate strong cash flow over the long term and focusing on future growth is just a mean to get there, hopefully faster.
With private companies where information can be scarce, asking direct questions to Management and understanding the cash cycle of the business is key before investing.
Understanding cash cycle will also generally help with the definition of net debt and debt-like items. Here are a few metrics that we’d recommend looking closely at to better understand the cash generation profile of the SaaS target.
Sales cycle
How long is the sales cycle ? In other words, how long does it take between finding a lead or marketing spending before a deal actually closes?
This is important because if you’re buying a high-touch sales business, you’ll likely start paying the salary of the sales people before you receive the revenue from the new customers. And if you want to scale and hire new sales people, this will create a through in cash that you need to account for.
If you’re running a low-touch sales business model, it’s also important to understand how long it will take after you spent money on digital marketing before it yields any result.
How fast is revenue generated?
After you have signed and on-boarded a new customer, it is important to understand if there is a ramp-up period, or on the contrary if for some reason the customer is likely to generate a higher level of revenue in the first few months.
Two good Saas metrics to look at that are both indicators of how fast revenue are generated and also how profitable customers are on average are :
- first 3 years LTV / Customer acquisition cost (CAC) => That will tell you how many times a customer will generate enough revenue to pay for the cost of its acquisition over a 3 year period
- First year LTV / CAC => used in combination with the metric above, it will give you a good indication of the ramp-up profile of customers, or on the contrary a good indication of how fast customers churn (if you do that analysis based on cohorts)
How fast is revenue collected?
Revenue collection is generally less of a problem for SaaS businesses that do not work with enterprise customers because a large part of SaaS operators use automated means of invoicing and payments like Stripe. However for companies still relying on invoicing, it is important to understand how long on average customers take to pay the invoices.
This is a matter of Net Working Capital management and calculating DSO (days of sales outstanding) in the company’s receivable account will help you better understand the cash generation profile of the company
Capex and reinvestment into the product (maintenance vs. development)
Another aspect of the company that has a huge impact on net cash flow is the spend requirement, or capex requirement, to maintain the product (i.e. bug fixing, updating technology stack, updating APIs and code to account for new technologies and security protocols being implemented) but also how much does the company have to invest each year to develop new features in order to maintain a strong revenue growth.
8 – Forecast: What Level of Comfort Can the SaaS Financials Demonstrate for Future Revenue Growth?
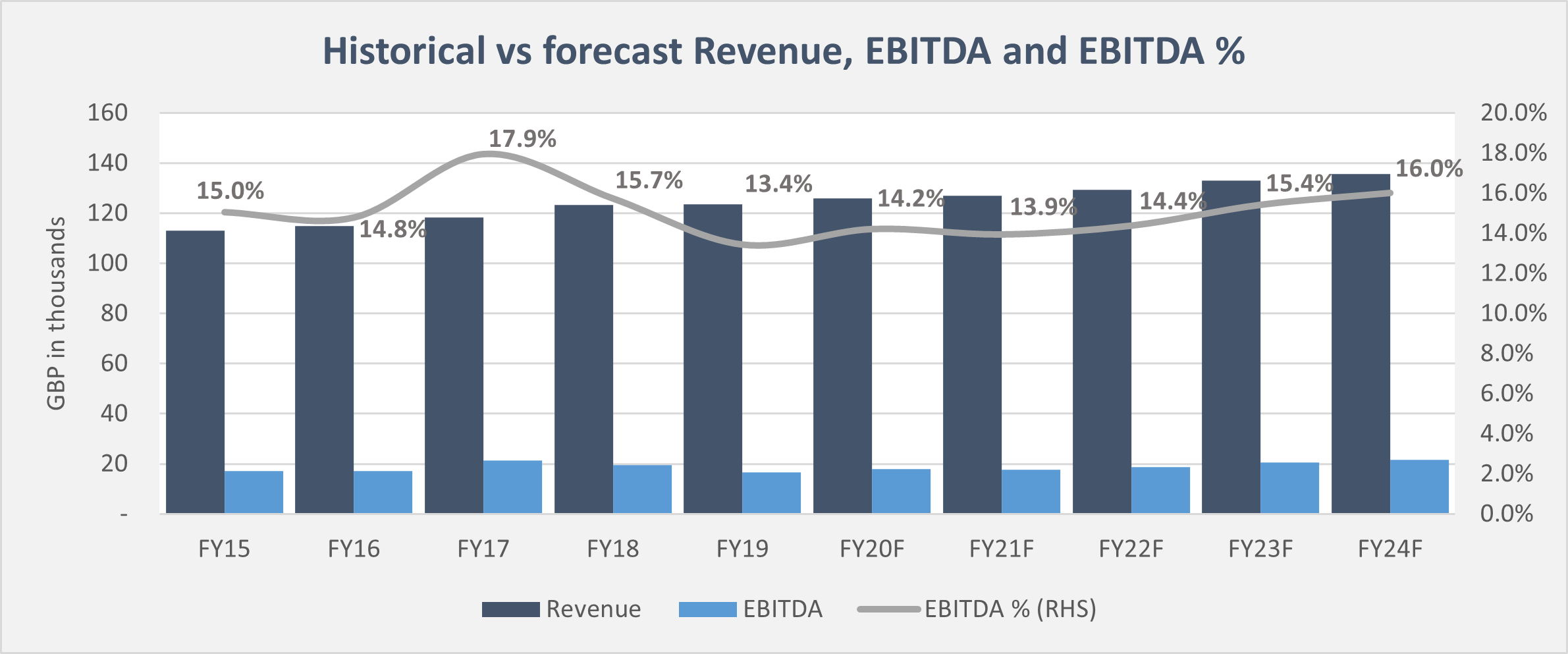
SaaS valuation as for any company valuation is based on the prospect of future cash flow.
In that regard, having accurate and reliable forecast is a strong element to be able to assess what current revenue multiple or ARR multiple to pay today to acquire the company.
While no one can predict the future and forecast achievability is always subject to systematic risks outside Management’s control, there are still ways to increase the level of comfort of a buyer.
One thing that can be done is to look at the SaaS budgeting process to understand how thorough it is done and whether or not operational team are involved in the process.
Another thing to do is to look at past annual budgets and compare them to the numbers actually achieved. If Management has consistently hit budget in the past, it will increase the investor’s confidence that they’re able to achieve their current forecast.
A third possibility to get comfort around forecast availability is to look at pipeline. This obviously apply only to companies which have longer and high touch sales cycles.
By looking at how many leads are in the pipeline, factor the stage each lead is at and calculated a weighted amount of new revenue that should be generated from these leads will help understand how close or how far the company is to hit their current annual revenue target.
9 – Commercial Due Diligence: How Attractive are the market dynamics?
The dynamics of the market are an essential factor that influence SaaS valuation and revenue multiples. To better understand the SaaS market, you may want to use expert due diligence professionals and strategy consultants which will do a full review of the market the SaaS business operates in, of competitors, market share, substitutes etc. A good way to do your own analysis is to follow the famous framework called “Porter’s 5 forces”.
In short, the commercial due diligence should help you understand how big is the market, how fast it is growing or shrinking, how competitive it is and how well position the target company is.
10 – Technical Due Diligence: How valuable is the product and technology the SaaS company is built on?
Outside of pure SaaS metrics and financials, the quality and complexity of the technology that the SaaS target offers can have a big impact on revenue multiple paid by investors.
For instance, Artificial Intelligence companies, that are generally built on complex and proprietary statistical and advanced neural network models, required a lot of work, are generally hard to copy or replicate, and can potentially deliver humongous value to the users.
In such case investors recognize the value of the technology and its commercial potential and may be ready to pay a higher revenue multiple to acquire that technology.
11 – Comparables: How are publicly traded SaaS companies and similar SaaS valuation metrics trending?
It may sound basic, but looking at relevant comparable transactions will help investors determine the average revenue multiples paid to acquire similar companies.
More often than not founders forget that SaaS is a business model and SaaS multiples are actually quite different based on the vertical the company operates on. Which is why it is useful to understand on a specific vertical what were the revenue or Ebitda multiples paid by investors.
In reality, revenue multiples paid by the market for a specific type of SaaS businesses will be a reflection of all the other points we mentioned in this article. Quality of SaaS metrics, market dynamics, quality of the technology, quality of the team etc.
You can also look at public Saas valuations, however if your company is private and significantly smaller (e.g. less than $200m ARR), keep in mind that investors apply a discount to account for smaller size and to account for reduced liquidity.
Additional must-do: Financial due diligence before acquiring SaaS businesses
If you take into consideration all the points listed above and do your diligence work correctly you should already be in a great position to articulate a detailed offer and narrow down the SaaS revenue multiple you are comfortable paying to acquire the company.
However before closing the deal, it is highly recommended to also get the help of seasoned consultants to perform the due diligence on all the areas of potential risks.
Once you have sorted your Financial Due Diligence, technical due diligence and commercial due diligence, you will be well inspired to hire a team of lawyers to also perform all the required legal due diligence and tax due diligence that may have an impact on the adjusted EBITDA, adjusted net debt and warranties that you’ll agree on before signing the purchase agreement.



